- Oracle Linux 8 Install Docker
- Oracle Linux 8 Install Docker Ubuntu
- Oracle Linux 8 Install Docker Centos
- Oracle Linux 8 Install Docker Linux
- Oracle Linux 8 Install Docker Usb
Oracle Linux Basic Support includes 24×7 access to log unlimited number of service requests via web or phone, integrated management features with Oracle Enterprise Manager and Spacewalk, XFS support, high availability with Oracle Clusterware, application and system containers with Docker and LXC, spacewalk support, and comprehensive tracing. Sure, you can use the Oracle provided Docker images or self created images too. But I have verified the Oracle repository today, the Dockerfile version is 19.3.0. And I don’t have the passion, to create new Dockerfiles for example to run 19.8 and download additional RU software.
- Introduction
- Oracle Linux
- Oracle Linux 7: Checking Yum Configuration
- Oracle Linux 8: About DNF and Application Stream
- Installing Software from Oracle Linux Yum Server
- Connecting To Yum Mirrors in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI)
- Oracle Linux
Oracle Linux yum server hosts software for Oracle Linux and compatible distributions. These instructions help you get started configuring your Linux system for Oracle Linux yum server and installing software via yum or dnf
Configuring Your System to Install Software from Oracle Linux Yum Server
If you are starting from scratch, and don’t have a Linux OS installed, download and install Oracle Linux. Alternatively, use an Oracle Linux Vagrant box to run with Oracle VM VirtualBox or KVM
Oracle Linux
In many cases, your Oracle Linux system will already be set up to install software from Oracle Linux yum server. See Installing Software from Oracle Linux Yum Server for an overview software available on this yum server. There have been some recent changes to Oracle Linux yum server, so it’s a good idea to check your configuration.
Oracle Linux 7
Checking Yum Configuration
Effective January of 2019, Oracle changed the way in which it distributes the configuration information for yum repositories provided by the Oracle Linux yum server. The original repository configuration, https://yum.oracle.com/public-yum-ol7.repo and https://yum.oracle.com/public-yum-ol6.repo will remain available for some time but are deprecated in favor of the new modularized approach.
To check that your system is using the new modular yum configuration, perform the following actions:
- Check that you have the appropriate base
oraclelinux-release-<rel>package installed for your Oracle Linux release. For example, on Oracle Linux 7, do:
- If
oraclelinux-release-<rel>is not installed, install it first:
- Check that you do not have an old monolithic
public-yum-<rel>.repoyum repository configuration file enabled. For example, on Oracle Linux 7, do:
- If this file exists and you have the base
oraclelinux-release-<rel>package installed, you may still need to run the/usr/bin/ol_yum_configure.shscript.
Oracle Linux 8
About DNF and Application Stream
The yum utility that is provided with Oracle Linux 8 is based on Dandified Yum (DNF). You can use dnf to install or upgrade RPM packages, while automatically handling package dependencies and requirements. The yum command that is provided with Oracle Linux 8 is a symbolic link to the dnf and you can use the dnf command and all of its options similarly to how you used the yum command on previous releases of Oracle Linux.
DNF introduces the concepts of modules, streams and profiles to allow for the management of different versions of software applications within a single operating system release. To read more about this subject, see the documentation: Oracle® Linux 8: DNF Modules and Application Stream
To see a list of available modules in Oracle Linux 8 Application Stream:
Red Hat Enterprise Linux, CentOS & Scientific Linux
To install software from Oracle Linux yum server on Red Hat Enterpise Linux, CentOS or Scientific Linux, perform these actions:

Import the Oracle Linux GPG key using these instructions.
Ceate a temporary yum repository configuration file
/etc/yum.repos.d/ol7-temp.repowith the following as the minimum required content:
- Install
oraclelinux-release-el7:
- Remove
ol7-temp.repoand any other remaining repo files that may conflict with Oracle Linux yum server:
You are now ready to install additional software. See: Installing Software from Oracle Linux Yum Server
Installing Software from Oracle Linux Yum Server
Oracle Linux yum server hosts many different types of software in repositories for which the configuration is installed and updated via release packages. Below is a list of available software and the corresponding release packages to configure yum.
Available Software

| Software | Release RPM |
|---|---|
Oracle Linux, UEK & Addons. In addition:
| oraclelinux-release-el8, oraclelinux-release-el7, oraclelinux-release-el6 |
| Oracle Linux patch repositories (for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure customers only) | oraclelinux-patchonly-release-el7, oraclelinux-patchonly-release-el6 |
| Software Collection Library for Oracle Linux | oracle-softwarecollection-release-el7, oracle-softwarecollection-release-el6 |
| Spacewalk Server | oracle-spacewalk-server-release-el7, oracle-spacewalk-server-release-el6 |
| Spacewalk Client | oracle-spacewalk-client-release-el7, oracle-spacewalk-client-release-el6 |
| Gluster Storage | oracle-gluster-release-el8, oracle-gluster-release-el7, oracle-gluster-release-el6 |
| Ceph Storage | oracle-ceph-release-el7 |
| Oracle Instant Client (release 21.x and newer) | oracle-instantclient-release-el8, oracle-instantclient-release-el7 |
| Oracle Instant Client (up to release 19.x) | oracle-release-el8, oracle-release-el7, oracle-release-el6 |
| EPEL for Oracle Linux | oracle-epel-release-el8, oracle-epel-release-el7 |
| Packages for Developers and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure | oraclelinux-developer-release-el8, oraclelinux-developer-release-el7, oraclelinux-developer-release-el6 |
| MySQL Community releases | mysql-release-el7, mysql-release-el6 |
| Stable releases of the Go programming language | oracle-golang-release-el7 |
| Stable PHP releases | oracle-php-release-el7, oracle-php-release-el6 |
| Stable Node.js releases | oracle-nodejs-release-el7, oracle-nodejs-release-el6 |
To see an up to date list of installed and available release packages on Oracle Linux 7:
or, on Oracle Linux 8:
Connecting To Yum Mirrors in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI)
Each region in Oracle Linux Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) has its own Oracle Linux yum server mirror to enable high speed access without incurring extra network charges. When launched, Oracle Linux images have a yum variable set in /etc/yum/vars/ociregion to ensure they connect to a mirror in the appropriate OCI region.
If /etc/yum/vars/ociregion is not set correctly, or not set correctly, run the following
Follow the steps covered in Checking Yum Configuration to verify your yum configuration.
Additional Software Available in OCI
The following software and release RPMs are available in OCI, in addition to the publicly available software.
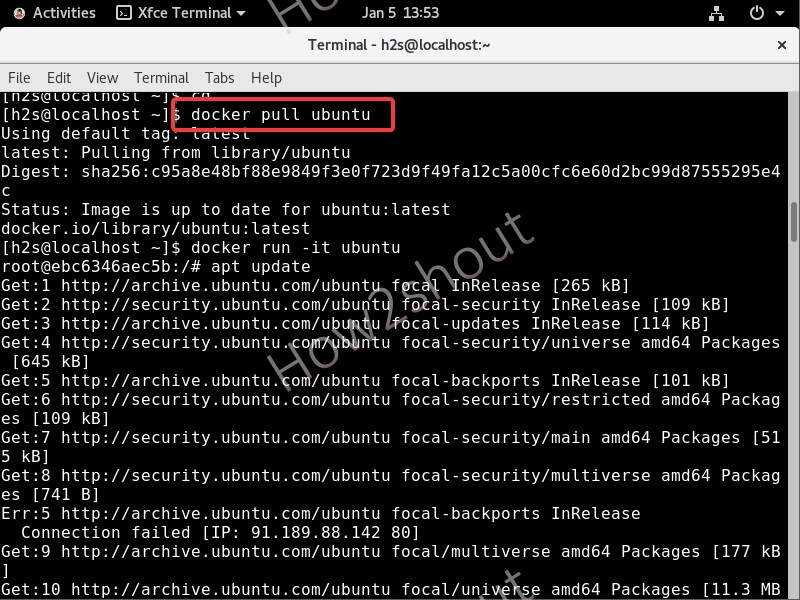
| Software | Release RPM |
|---|---|
| Oracle Linux patch repositories | oraclelinux-patchonly-release-el7, oraclelinux-patchonly-release-el6 |
| Ksplice Utilities | oracle-ksplice-release-el7, oracle-ksplice-release-el6 |
Oracle Linux 8 Install Docker
References

Oracle Linux 8 Install Docker Ubuntu
- Blog post: Modularizing the Oracle Linux yum server Repository Configurations
- 2.5.1 Installing MySQL on Linux Using the MySQL Yum Repository
- 2.5.2 Installing MySQL on Linux Using the MySQL APT Repository
- 2.5.3 Installing MySQL on Linux Using the MySQL SLES Repository
- 2.5.4 Installing MySQL on Linux Using RPM Packages from Oracle
- 2.5.5 Installing MySQL on Linux Using Debian Packages from Oracle
- 2.5.6 Deploying MySQL on Linux with Docker
- 2.5.7 Installing MySQL on Linux from the Native Software Repositories
- 2.5.8 Installing MySQL on Linux with Juju
- 2.5.9 Managing MySQL Server with systemd
Oracle Linux 8 Install Docker Centos
Linux supports a number of different solutions for installing MySQL. We recommend that you use one of the distributions from Oracle, for which several methods for installation are available:
Table 2.8 Linux Installation Methods and Information
| Type | Setup Method | Additional Information |
|---|---|---|
| Apt | Enable the MySQL Apt repository | Documentation |
| Yum | Enable the MySQL Yum repository | Documentation |
| Zypper | Enable the MySQL SLES repository | Documentation |
| RPM | Download a specific package | Documentation |
| DEB | Download a specific package | Documentation |
| Generic | Download a generic package | Documentation |
| Source | Compile from source | Documentation |
| Docker | Use the Oracle Container Registry. You can also use Docker Hub for MySQL Community Edition and My Oracle Support for MySQL Enterprise Edition. | Documentation |
| Oracle Unbreakable Linux Network | Use ULN channels | Documentation |
Oracle Linux 8 Install Docker Linux
As an alternative, you can use the package manager on your system to automatically download and install MySQL with packages from the native software repositories of your Linux distribution. These native packages are often several versions behind the currently available release. You are also normally unable to install development milestone releases (DMRs), since these are not usually made available in the native repositories. For more information on using the native package installers, see Section 2.5.7, “Installing MySQL on Linux from the Native Software Repositories”.
Oracle Linux 8 Install Docker Usb
For many Linux installations, you want to set up MySQL to be started automatically when your machine starts. Many of the native package installations perform this operation for you, but for source, binary and RPM solutions you may need to set this up separately. The required script, mysql.server, can be found in the support-files directory under the MySQL installation directory or in a MySQL source tree. You can install it as /etc/init.d/mysql for automatic MySQL startup and shutdown. See Section 4.3.3, “mysql.server — MySQL Server Startup Script”.